Arxiv Dives
Every Friday at Oxen.ai we host a paper club called "Arxiv Dives" to make us smarter Oxen 🐂 🧠. We believe diving into the details of research papers is the best way to build fundamental knowledge, spot patterns and keep up with the bleeding edge.
In Arxiv Dives, we cover state of the art research papers, and dive into the gnitty gritty details of how AI models work. From the math to the data to the model architecture, we cover it all.
Modeling sequences with infinite context length is one of the dreams of Large Language models. Some LLMs such as Transformers suffer from quadratic computational complexity, making...

The ability to interpret and steer large language models is an important topic as they become more and more a part of our daily lives. As the leader in AI safety, Anthropic takes o...

Diffusion Transformers have been gaining a lot of steam since OpenAI's demo of Sora back in March. The problem, when we think of training text-to-image models, we usually think mil...

Large Language Models have shown very good ability to generalize within a distribution, and frontier models have shown incredible flexibility under prompting. Now that there is so...

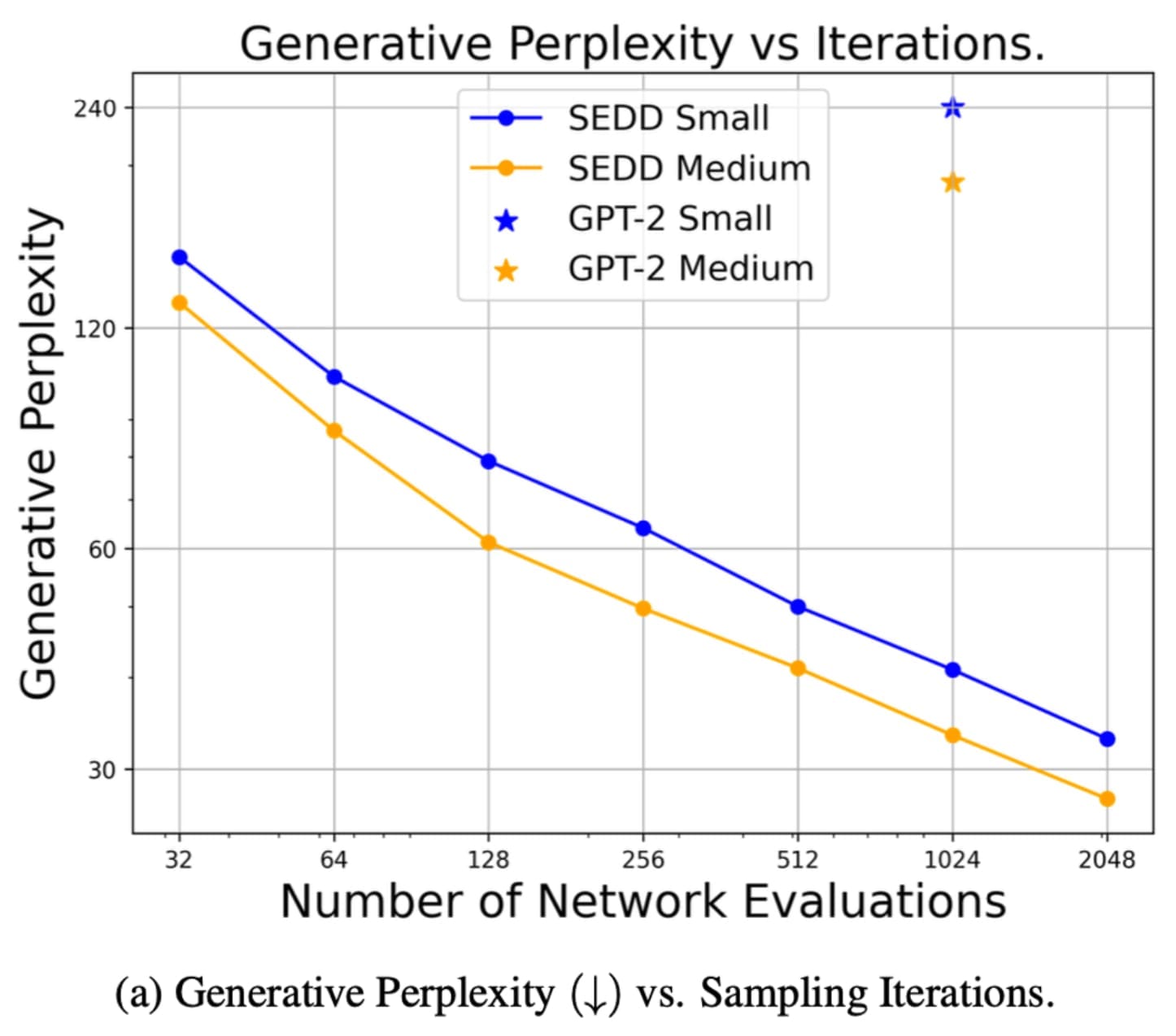
This is part two of a series on Diffusion for Text with Score Entropy Discrete Diffusion (SEDD) models. Today we will be diving into the code for diffusion models for text, and see...

Diffusion models have been popular for computer vision tasks. Recently models such as Sora show how you can apply Diffusion + Transformers to generate state of the art videos with ...

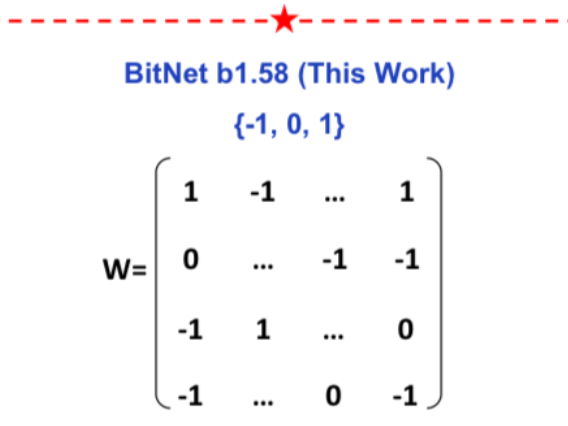
This paper presents BitNet b1.58 where every weight in a Transformer can be represented as a {-1, 0, 1} instead of a floating point number. The model matches full precision transfo...

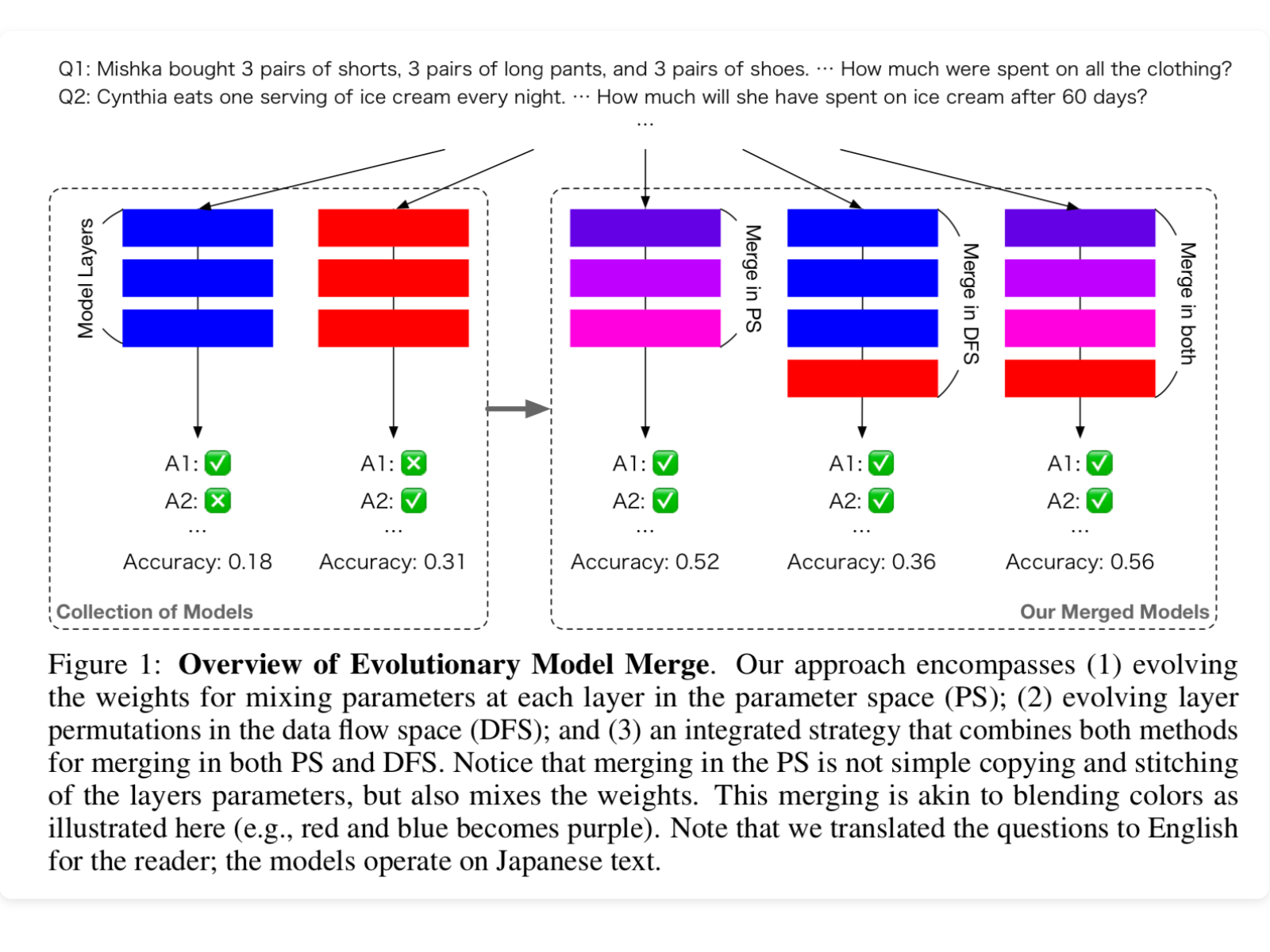
Today, we’re diving into a fun paper by the team at Sakana.ai called “Evolutionary Optimization of Model Merging Recipes”. The high level idea is that we have so many open weights ...

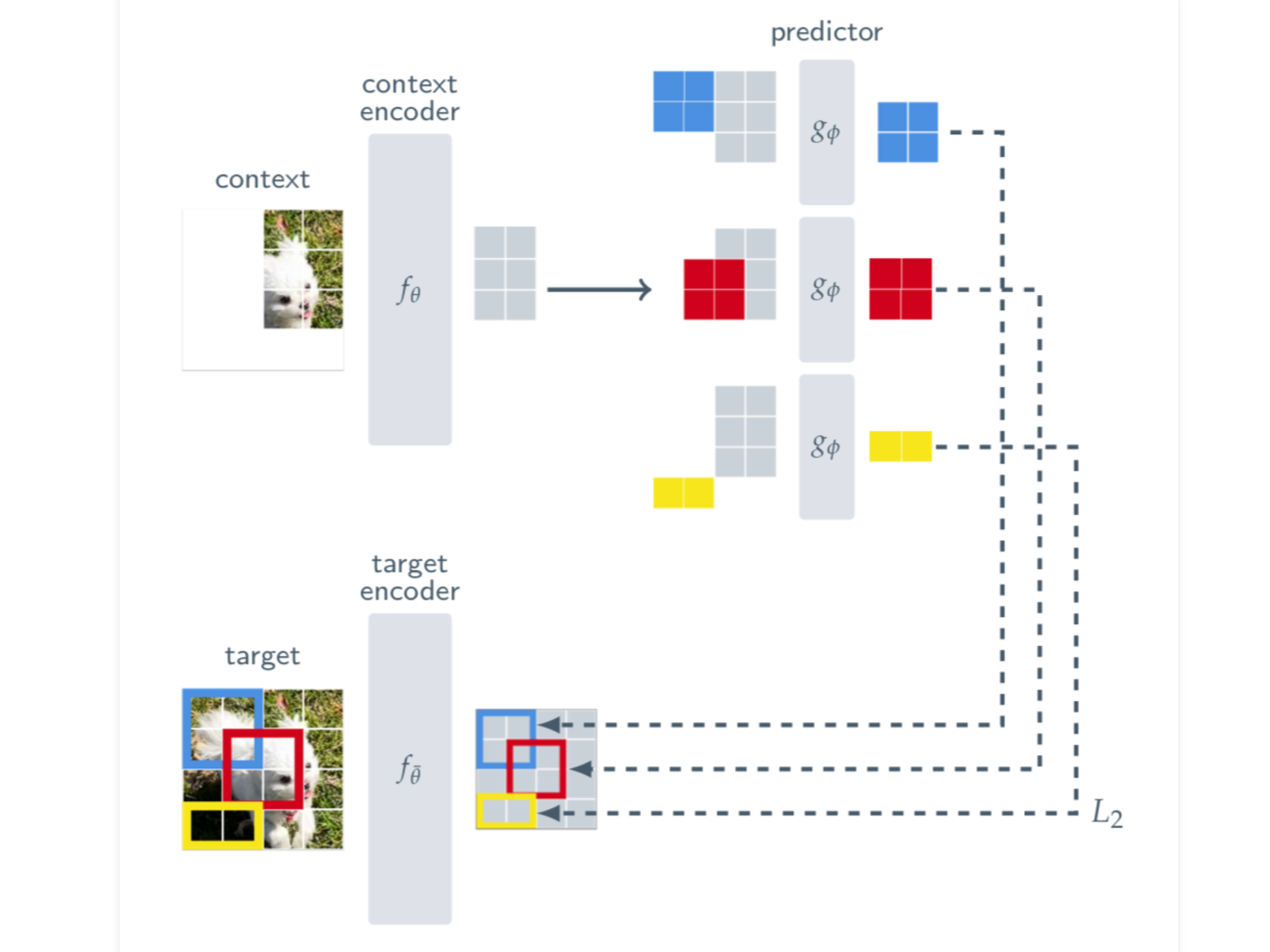
Today, we’re diving into the I-JEPA paper. JEPA stands for Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture and if you have been following Yann LeCunn, is a technique he has been hyping up ...

Diffusion transformers achieve state-of-the-art quality generating images by replacing the commonly used U-Net backbone with a transformer that operates on latent patches. They rec...